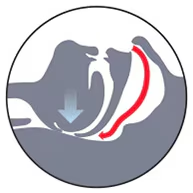
About sleep-disordered breathing
Sleep-disordered breathing (SDB) is characterised by abnormal respiratory patterns, or pauses in breathing, and insufficient ventilation during sleep.
Some of the most common types of sleep-disordered breathing include upper airway resistance syndrome (UARS), and obstructive sleep apnoea-hypopnea syndrome* (OSAHS), also known as obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA).

Comorbidities associated with sleep apnoea
1. Sleep apnoea and hypertension
People with sleep-disordered breathing (SDB) have an increased risk of developing hypertension, independent of other relevant risk factors.1-5 This risk is related to SDB severity: the more severe the SDB, the greater the risk of developing hypertension.
During healthy sleep, blood pressure decreases, but SDB patients instead tend to experience:
- elevated blood pressure during sleep;
- prolonged cardiovascular stress, which can lead to increased blood pressure also occurring during the day.
SDB is present in more than 30% of patients with hypertension,6 and in around 80% of patients with drug resistant hypertension.5 For this group of patients in particular, treatment with positive airway pressure therapy may be especially important.7
Obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA) is the most common form of sleep-disordered breathing (SDB), affecting more than three in ten men and nearly one in five women.1 Patients who suffer from OSA often experience partial or full upper airway collapse during sleep.
2. Sleep apnoea and heart failure
Up to 50% of heart failure patients experience moderate to severe sleep-disordered breathing (SDB),8 in the form of central sleep apnoea (CSA), Cheyne-Stokes respiration (CSR), obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA) or a combination thereof.9
Cheyne-Stokes respiration (CSR) occurs when periods of hyperventilation and hypoventilation (in a waxing/waning breathing pattern) alternate with periods of central hypopnoea/apnoea.
CSR is a common form of SDB in patients with severe left ventricular dysfunction.10
It’s thought that SDB and CSR accelerate the progression of heart failure by causing:
– Repetitive hypoxia;
– Increased afterload;
– Increased sympathetic activity;11
– Oscillations in heart rate and blood pressure.
Fragmented sleep resulting from CSR also causes fatigue and daytime sleepiness, which impacts quality of life.
3. Sleep apnoea and stroke
The majority of patients who have experienced a stroke and transient ischemic attack also have SDB,14 which is sometimes undiagnosed. As stroke patients with SDB also have worse functional outcomes15, you should consider screening for SDB16 when investigating the stroke. Stroke has the potential to cause SDB, by either affecting:
- central mechanisms resulting in central sleep apnoea;
- muscle tone resulting in obstructive sleep apnoea.
People with sleep apnoea may be predisposed to stroke through a number of symptoms they experience. In particular:
- Repetitive drops in nocturnal blood oxygen levels caused by sleep apnoea can result in intermittent hypoxia which has been shown to be associated with systemic inflammation.17
- Sleep fragmentation from sleep apnoea results in hypersympathetic activity.18
Recognising sleep apnoea in stroke survivors is often challenging because the symptoms associated with sleep apnoea are often attributed to strokes. A complete sleep history from family members can help you determine whether sleep apnoea was present prior to the stroke or developed after the stroke.
4. Sleep apnoea and type 2 diabetes
Sleep apnoea is common among patients with type 2 diabetes.19 It is independently associated with insulin resistance, glucose intolerance and metabolic syndrome,20-22 and when untreated, can lead to poor overall treatment outcomes.
However, despite the number of type 2 diabetes patients with SDB, it largely goes undiagnosed.
Screen your patients for type 2 diabetes and sleep apnoea
As a result of accumulated research, the International Diabetes Federation recognises the association between type 2 diabetes and sleep apnoea, and recommends routinely screening OSA patients for type 2 diabetes, and screening type 2 diabetes patients displaying sleep apnoea symptoms for OSA.
As patients with sleep apnoea and patients with diabetes share similar comorbidities, screening both ways is recommended: check for sleep apnoea in diabetes patients, and check for diabetes in patients with sleep apnoea.23
5. Sleep apnoea and COPD
Obstructive Sleep Apnoea and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) are two diseases that often coexist within a patient.
COPD is a condition that describes the progressive deterioration of the respiratory system by pulmonary airway obstruction, emphysema and decreased airflow. COPD also refers to lung disorders such as chronic bronchitis, and in some cases, chronic asthma.
According to the American Thoracic Society, patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) have a higher prevalence of sleep disorders than the general population, with close to 50% of patients reporting significant disturbance in sleep quality.
Co-existence of both COPD and OSA occurs in 1% of adults.24
COPD and OSA are often coined as overlap syndrome. Both COPD and OSA are independent risk factors for the following:
– Arrhythmia;
– High blood pressure;
– Heart attack;
– Stroke;
– Other cardiovascular disease.
Studies have shown that patients with untreated overlap syndrome have a higher mortality rate1. We at Resmed strive to impact comorbidity and improve quality of life. We offer a range of treatment options to alleviate the symptoms of COPD.
References:
* An apnoea refers to a pause in respiration lasting more than 10 seconds.A hypopnoea is defined as a decrease in airflow of at least 30% for 10 seconds or more,with an associated oxygen desaturation or arousal.
- Peppard PE et al. N Engl J Med. 2000
- Lavie P et al. BMJ. 2000
- Nieto FJ, Young TB et al. JAMA. 2000
- Bixler EO, Vgontzas AN at al. Arch Intern Med. 2000
- Marin JM et al. JAMA. 2012
- Logan AG, Perlikowski SM et al. J Hypertens. 2001
- Montesi et al. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine. 2012
- Bitter T. et al, EJHF, 2009
- Oldenburg O et al. Circ J 2012
- Lanfranchi PA et al. Circulation. 2003
- Garcia-Touchard A et al. Chest. 2008
- Javaheri S et al. AJRCCM. 2011
- Javaheri S et al. J Am Col Cardiol. 2007
- Johnson KG, et al. J Clin Sleep Med. 2010
- Martínez-García MA, et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009
- Wessendorf TE, et al. J Neurol. 2000
- Drager LF, et al. Chest. 2011
- Jelic S, et al. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2008
- Einhorn et al. Endocr Pract. 2007
- Aronsohn et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010
- Punjabi et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002
- Coughlin et al. Eur Heart J. 2004
- International Diabetes Federation. The IDF consensus statement on sleep apnoea and type 2 diabetes. Brussels, Belgium: International Diabetes Federation; 2008
- Ruth Lee, Walter T. McNicholas. Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patients. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2011;17(2):79–83.